Architecture
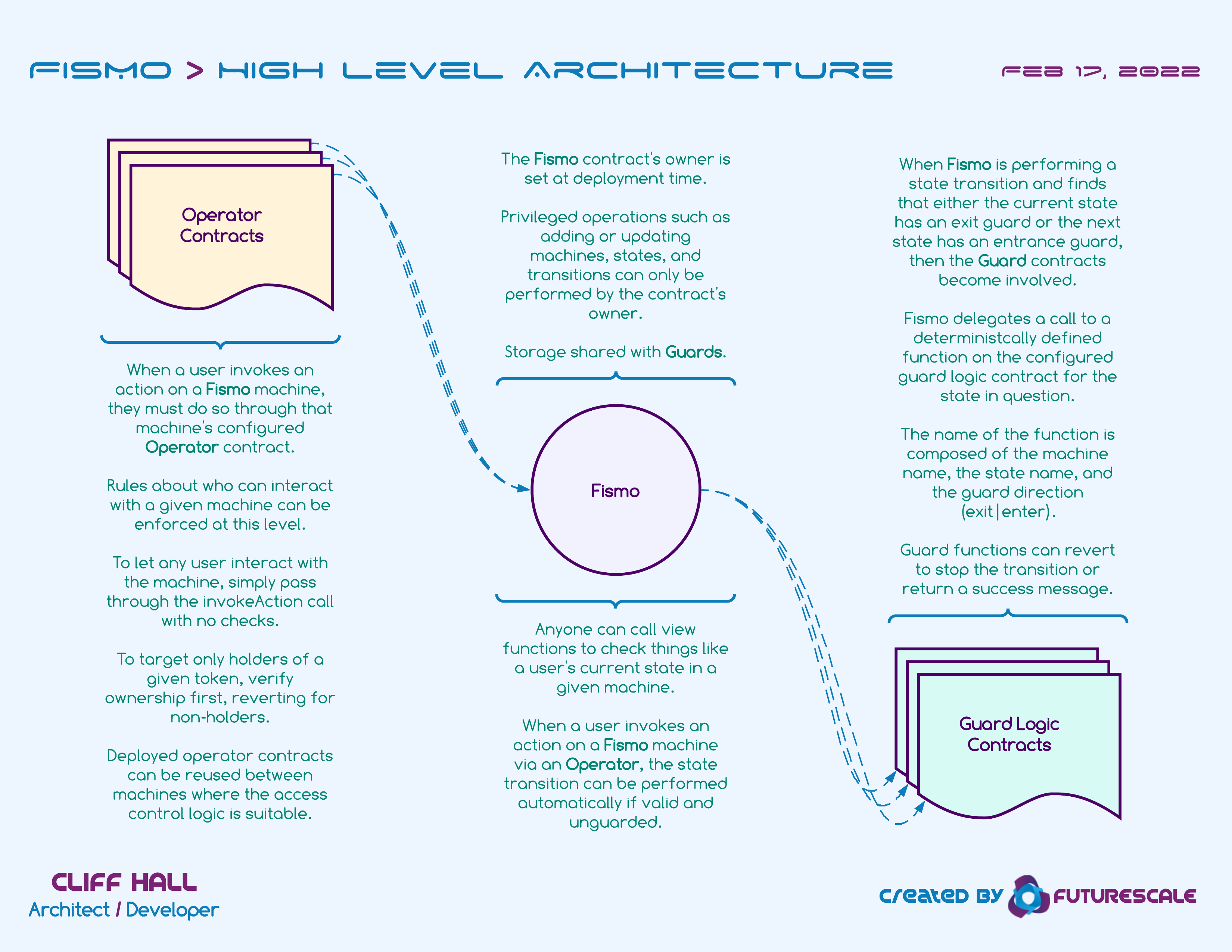
Actors
Operator
-
When a user invokes an action on a Fismo machine, they must do so through that machine’s configured Operator contract.
-
Rules about who can interact with a given machine can be enforced at this level.
-
To let any user interact with the machine, simply pass through the invokeAction call with no checks.
-
To target only holders of a given token, verify ownership first, reverting for non-holders.
-
Deployed operator contracts can be reused between machines where the access control logic is suitable.
Fismo
-
The Fismo contract’s owner is set at deployment time.
-
Privileged operations such as adding or updating machines, states, and transitions can only be performed by the contract’s owner.
-
Storage shared with Guards.
-
Anyone can call view functions to check things like a user’s current state in a given machine.
-
When a user invokes an action on a Fismo machine via an Operator, the state transition can be performed automatically if valid and unguarded.
Guard
-
When Fismo is performing a state transition and finds that either the current state has an exit guard or the next state has an entrance guard, then the Guard contracts become involved.
-
Fismo delegates a call to a deterministcally defined function on the configured guard logic contract for the state in question.
-
The name of the function is composed of the machine name, the state name, and the guard direction, i.e., exit, enter.
-
Guard functions can revert to stop the transition or return a success message.